Introduction
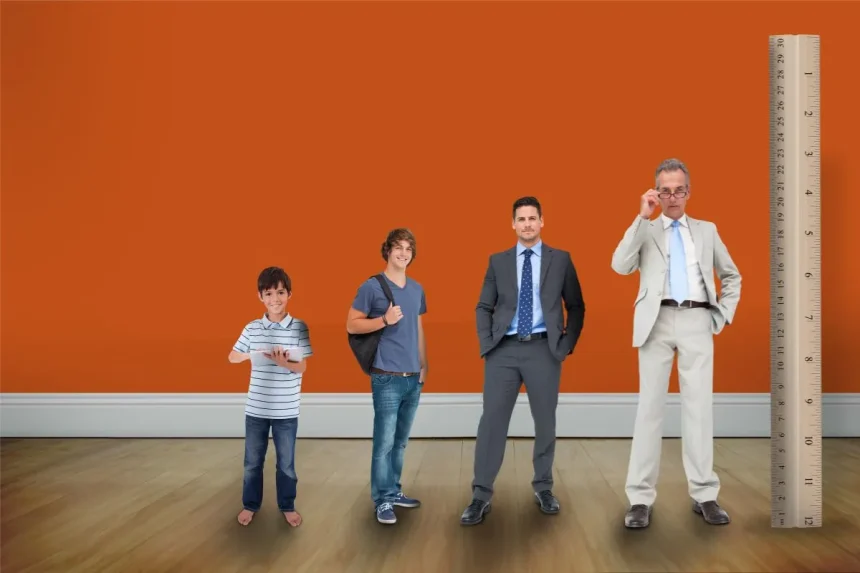
The journey through male life stages is marked by distinct physical, emotional, and social changes. From adolescence to old age, each stage presents unique challenges and opportunities that shape a man’s health, lifestyle, and overall well-being. Understanding these transitions can empower men to make informed decisions and lead healthier lives. This article delves into the various male life stages, highlighting key health considerations, lifestyle adjustments, and common challenges faced along the way.
1. Adolescence (13-19 Years)
Health Considerations:
During adolescence, boys undergo significant physical changes due to puberty, including growth spurts, voice changes, and increased muscle mass. This stage is crucial for building healthy habits, as diet, exercise, and mental health can significantly impact long-term well-being. Mental health issues like anxiety and depression can emerge, often influenced by peer pressure, academic stress, and body image concerns.
Lifestyle Tips:
- Encourage regular physical activity to promote healthy growth and reduce stress.
- Focus on a balanced diet rich in nutrients essential for development, such as calcium, iron, and protein.
- Establish a routine that includes sufficient sleep, as rest is vital for both physical and mental health.
Challenges:
Adolescents may face challenges related to identity, self-esteem, and peer relationships. Navigating social media, academic pressures, and family expectations can also be stressful.
2. Young Adulthood (20-39 Years)
Health Considerations:
Young adulthood is often characterized by peak physical health, but it’s also a time when lifestyle habits can set the stage for future health outcomes. Issues such as stress, poor diet, lack of exercise, and risky behaviors (e.g., smoking, excessive alcohol use) can begin to take a toll. Sexual health and family planning also become prominent concerns during this phase.
Lifestyle Tips:
- Maintain a balanced diet and stay active to manage weight and prevent chronic diseases.
- Monitor mental health, as this stage can be marked by career stress and relationship dynamics.
- Prioritize regular check-ups and screenings to detect potential health issues early.
Challenges:
Common challenges include career pressures, establishing long-term relationships, and managing finances. Balancing work, social life, and self-care can be difficult but is crucial for overall well-being.
3. Middle Adulthood (40-59 Years)
Health Considerations:
Middle adulthood often brings about changes such as decreased metabolism, weight gain, and the onset of chronic conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and heart disease. This stage is also when men may begin to experience a decline in testosterone levels, affecting energy, mood, and sexual health.
Lifestyle Tips:
- Focus on heart health by adopting a diet low in saturated fats and high in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Engage in regular strength training and cardiovascular exercise to maintain muscle mass and cardiovascular fitness.
- Manage stress through mindfulness, hobbies, or professional support, as mental health can be impacted by work and family responsibilities.
Challenges:
This life stage can be marked by a sense of crisis or dissatisfaction, often termed as a “midlife crisis.” Men may grapple with aging, career stagnation, and changing family dynamics as children grow up and parents age.
4. Late Adulthood (60+ Years)
Health Considerations:
In late adulthood, men face age-related declines in physical and cognitive function. Common health concerns include arthritis, osteoporosis, cardiovascular issues, and prostate problems. Cognitive decline and mental health issues, such as loneliness and depression, can also become prominent.
Lifestyle Tips:
- Engage in low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, and yoga to maintain mobility and reduce joint strain.
- Prioritize a diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats to support heart health and digestion.
- Stay mentally active through reading, puzzles, social activities, and continued learning to maintain cognitive function.
Challenges:
Retirement, loss of loved ones, and declining health can lead to feelings of isolation and reduced self-worth. It’s important for older men to stay socially connected and seek purpose through hobbies, volunteering, or part-time work.
Conclusion
Understanding the unique health, lifestyle, and challenges associated with each male life stage can empower men to make proactive choices for their well-being. By addressing the specific needs of each stage, men can navigate their journey with confidence, ensuring a healthier and more fulfilling life at every age.
Get more info: https://www.timelinetale.com/